# Sliders
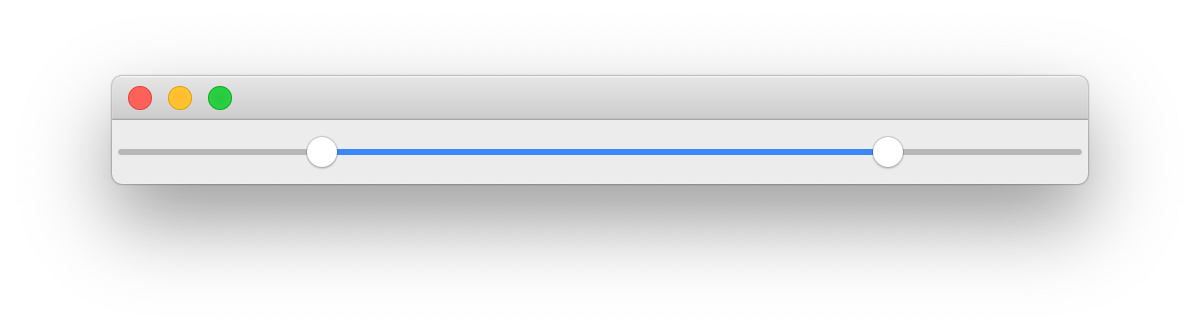
- `QRangeSlider` inherits from [`QSlider`](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qslider.html)
and attempts to match the Qt API as closely as possible
- Uses platform-specific styles (for handle, groove, & ticks) but also supports
QSS style sheets.
- Supports mouse wheel and keypress (soon) events
- Supports more than 2 handles (e.g. `slider.setValue([0, 10, 60, 80])`)
------
## Range Slider
```python
from superqt import QRangeSlider
# as usual:
# you must create a QApplication before create a widget.
range_slider = QRangeSlider()
```
As `QRangeSlider` inherits from `QtWidgets.QSlider`, you can use all of the
same methods available in the [QSlider API](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qslider.html). The major difference is that `value` and `sliderPosition` are reimplemented as `tuples` of `int` (where the length of the tuple is equal to the number of handles in the slider.)
### `value: Tuple[int, ...]`
This property holds the current value of all handles in the slider.
The slider forces all values to be within the legal range:
`minimum <= value <= maximum`.
Changing the value also changes the sliderPosition.
##### Access Functions:
```python
range_slider.value() -> Tuple[int, ...]
```
```python
range_slider.setValue(val: Sequence[int]) -> None
```
##### Notifier Signal:
```python
valueChanged(Tuple[int, ...])
```
### `sliderPosition: Tuple[int, ...]`
This property holds the current slider positions. It is a `tuple` with length equal to the number of handles.
If [tracking](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qabstractslider.html#tracking-prop) is enabled (the default), this is identical to [`value`](#value--tupleint-).
##### Access Functions:
```python
range_slider.sliderPosition() -> Tuple[int, ...]
```
```python
range_slider.setSliderPosition(val: Sequence[int]) -> None
```
##### Notifier Signal:
```python
sliderMoved(Tuple[int, ...])
```
### Additional properties
These options are in addition to the Qt QSlider API, and control the behavior of the bar between handles.
| getter | setter | type | default | description |
| -------------------- | ------------------------------------------- | ------ | ------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `barIsVisible` | `setBarIsVisible`
`hideBar` / `showBar` | `bool` | `True` | Whether the bar between handles is visible. |
| `barMovesAllHandles` | `setBarMovesAllHandles` | `bool` | `True` | Whether clicking on the bar moves all handles or just the nearest |
| `barIsRigid` | `setBarIsRigid` | `bool` | `True` | Whether bar length is constant or "elastic" when dragging the bar beyond min/max. |
------
### Examples
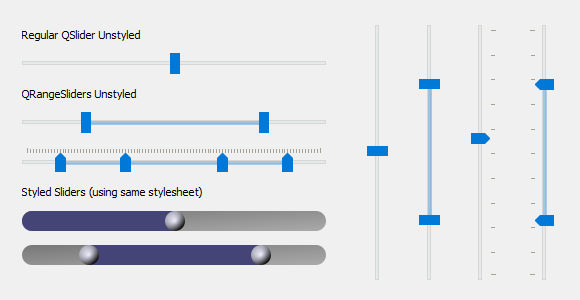
These screenshots show `QRangeSlider` (multiple handles) next to the native `QSlider`
(single handle). With no styles applied, `QRangeSlider` will match the native OS
style of `QSlider` – with or without tick marks. When styles have been applied
using [Qt Style Sheets](https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/stylesheet-reference.html), then
`QRangeSlider` will inherit any styles applied to `QSlider` (since it inherits
from QSlider). If you'd like to style `QRangeSlider` differently than `QSlider`,
then you can also target it directly in your style sheet. The one "special"
property for QRangeSlider is `qproperty-barColor`, which sets the color of the
bar between the handles.
> The code for these example widgets is [here](../examples/demo_widget.py)
See style sheet used for this example
```css
/*
Because QRangeSlider inherits from QSlider, it will also inherit styles
*/
QSlider {
min-height: 20px;
}
QSlider::groove:horizontal {
border: 0px;
background: qlineargradient(x1:0, y1:0, x2:1, y2:1,
stop:0 #777, stop:1 #aaa);
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
QSlider::handle {
background: qradialgradient(cx:0, cy:0, radius: 1.2, fx:0.5,
fy:0.5, stop:0 #eef, stop:1 #000);
height: 20px;
width: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
/*
"QSlider::sub-page" is the one exception ...
(it styles the area to the left of the QSlider handle)
*/
QSlider::sub-page:horizontal {
background: #447;
border-top-left-radius: 10px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 10px;
}
/*
for QRangeSlider: use "qproperty-barColor". "sub-page" will not work.
*/
QRangeSlider {
qproperty-barColor: #447;
}
```
#### macOS
##### Catalina

##### Big Sur

#### Windows
#### Linux

## Labeled Sliders
This package also includes two "labeled" slider variants. One for `QRangeSlider`, and one for the native `QSlider`:
### `QLabeledRangeSlider`

```python
from superqt import QLabeledRangeSlider
```
This has the same API as `QRangeSlider` with the following additional options:
#### `handleLabelPosition`/`setHandleLabelPosition`
Where/whether labels are shown adjacent to slider handles.
**type:** `QLabeledRangeSlider.LabelPosition`
**default:** `LabelPosition.LabelsAbove`
*options:*
- `LabelPosition.NoLabel` (no labels shown adjacent to handles)
- `LabelPosition.LabelsAbove`
- `LabelPosition.LabelsBelow`
- `LabelPosition.LabelsRight` (alias for `LabelPosition.LabelsAbove`)
- `LabelPosition.LabelsLeft` (alias for `LabelPosition.LabelsBelow`)
#### `edgeLabelMode`/`setEdgeLabelMode`
**type:** `QLabeledRangeSlider.EdgeLabelMode`
**default:** `EdgeLabelMode.LabelIsRange`
*options:*
- `EdgeLabelMode.NoLabel`: no labels shown at slider extremes
- `EdgeLabelMode.LabelIsRange`: edge labels shown the min/max values
- `EdgeLabelMode.LabelIsValue`: edge labels shown the slider range
#### fine tuning position of labels:
If you find that you need to fine tune the position of the handle labels:
- `QLabeledRangeSlider.label_shift_x`: adjust horizontal label position
- `QLabeledRangeSlider.label_shift_y`: adjust vertical label position
### `QLabeledSlider`

```python
from superqt import QLabeledSlider
```
(no additional options at this point)
## Issues
If you encounter any problems, please [file an issue] along with a detailed
description.
[file an issue]: https://github.com/napari/superqt/issues
## Float Slider
just like QSlider, but supports float values
```python
from superqt import QDoubleSlider
```